Tax Brackets Explained: How They Impact Your Finances And Why You Should Care
So here we are, diving headfirst into the world of tax brackets. Now, I know what you're thinking—taxes? Really? But hear me out, because this is crucial stuff. Tax brackets might sound boring, but they're the backbone of how much money stays in your pocket at the end of the year. Yeah, you read that right. Understanding these brackets can save you a ton of cash and help you plan for the future. It's like having a secret weapon in your financial arsenal.
Let’s break it down. Tax brackets are essentially ranges of income that are taxed at different rates. Think of them as steps on a ladder. The more money you make, the higher up the ladder you climb, and the more you pay in taxes. But here’s the kicker—it’s not as simple as just paying one flat rate. Each bracket has its own percentage, and that’s where things get interesting. Stick around, because we’re about to demystify the whole thing.
Now, before you zone out, let’s talk about why this matters to you. Whether you're a fresh graduate or a seasoned professional, understanding tax brackets can make a huge difference in your financial health. It’s not just about saving money—it’s about making informed decisions. Ready to dive in? Let’s go.
Read also:Joplin Tornado Article The Devastation And Resilience Unveiled
Understanding Tax Brackets: The Basics
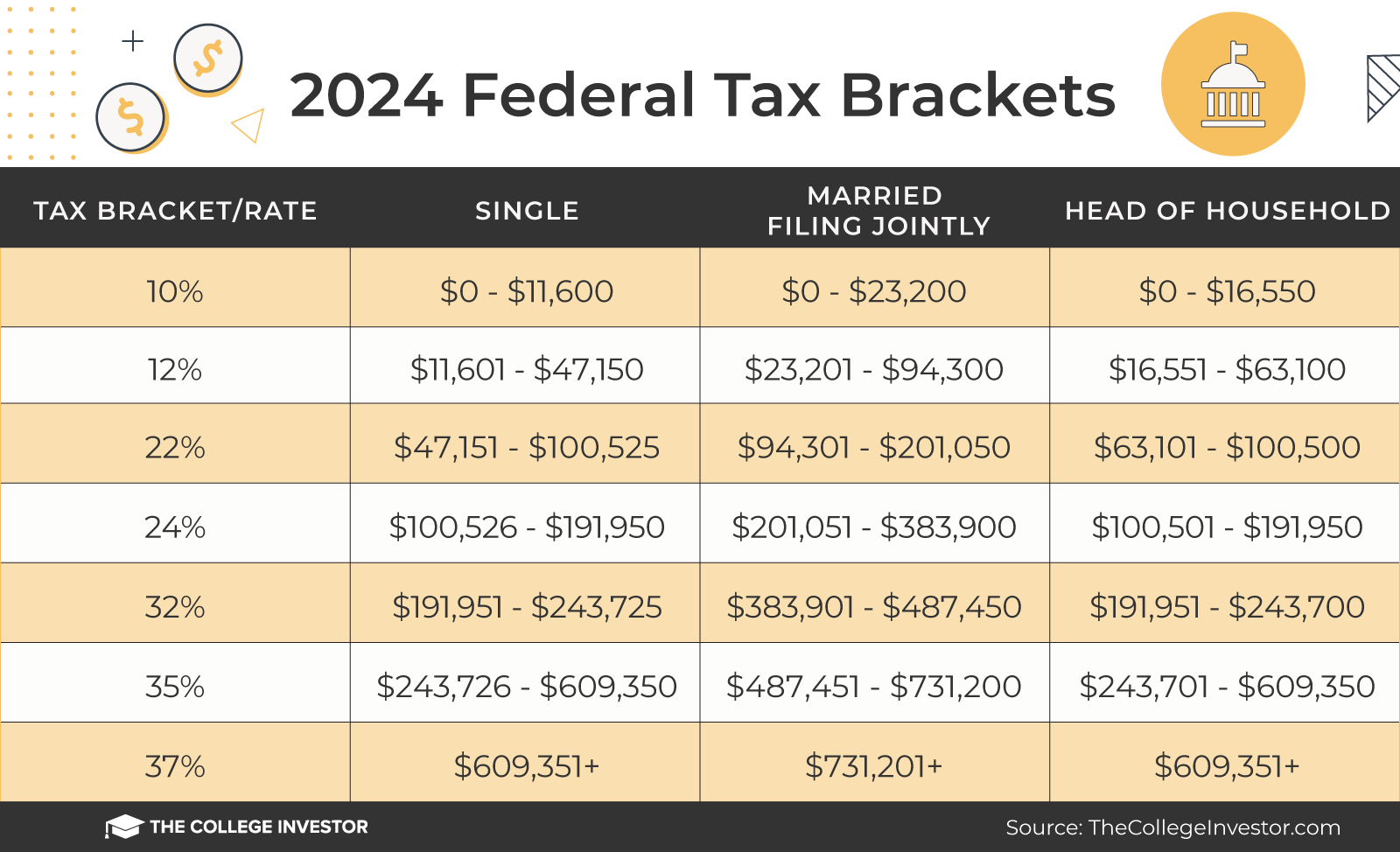
Alright, let’s start with the basics. Tax brackets are basically a system the government uses to determine how much tax you owe based on your income. The U.S. tax system is progressive, meaning that the more you earn, the more you pay. But here’s the thing—it’s not like you pay the same rate on all your income. Instead, different portions of your income are taxed at different rates. Confusing? Don’t worry, we’ll break it down step by step.
How Tax Brackets Work
Here’s the deal: tax brackets are divided into ranges, and each range has its own tax rate. For example, if you’re single and you earn $50,000 in 2023, the first $11,000 of your income might be taxed at 10%, the next chunk at 12%, and so on. This is called marginal tax rate. So, even if you’re in the 22% tax bracket, it doesn’t mean all your income is taxed at 22%. Only the portion that falls within that bracket is taxed at that rate. Make sense?
- Income up to $11,000: 10% tax rate
- Income between $11,001 and $44,725: 12% tax rate
- Income between $44,726 and $95,375: 22% tax rate
And so it goes, climbing higher as your income increases. But here’s the good news: most people don’t end up paying the top rate on all their income. That’s why understanding how these brackets work is so important.
Why Tax Brackets Matter to You
Now, you might be wondering, “Why should I care about tax brackets?” Well, my friend, it’s simple. Tax brackets directly affect how much money you take home. They determine how much of your hard-earned cash goes to Uncle Sam and how much stays in your wallet. Ignoring them could mean missing out on potential savings or even overpaying your taxes. And who wants to do that?
Impact on Your Take-Home Pay
Let’s put it into perspective. Say you get a raise at work. Great news, right? But if that raise pushes you into a higher tax bracket, you might end up taking home less than you expected. That’s because the extra income you earn will be taxed at a higher rate. However, the good news is that only the portion of your income that falls into the higher bracket is taxed at that rate. The rest stays the same. So, it’s not all doom and gloom.
How Tax Brackets Affect Different Income Levels
Here’s where things get interesting. Tax brackets don’t treat everyone the same. Depending on your filing status—whether you’re single, married filing jointly, or head of household—the brackets can vary. Let’s break it down by income level.
Read also:Madeleine Beth Mccann Born The Story That Gripped The World
Single Filers
If you’re single, the tax brackets look something like this:
- Up to $11,000: 10% tax rate
- $11,001 to $44,725: 12% tax rate
- $44,726 to $95,375: 22% tax rate
- $95,376 to $182,100: 24% tax rate
As you can see, the rates increase as your income goes up. But remember, only the portion of your income that falls into each bracket is taxed at that rate. So, if you earn $50,000, you’re not paying 22% on all of it.
Married Filing Jointly
For those who are married and filing jointly, the brackets are a bit more forgiving:
- Up to $22,000: 10% tax rate
- $22,001 to $89,450: 12% tax rate
- $89,451 to $190,750: 22% tax rate
- $190,751 to $364,200: 24% tax rate
See how the numbers are higher? That’s because married couples typically have more combined income, so the brackets are adjusted accordingly.
Common Misconceptions About Tax Brackets
There are a lot of myths floating around about tax brackets. Let’s clear some of them up. One common misconception is that if you move into a higher tax bracket, all your income gets taxed at that higher rate. Not true. Only the portion of your income that falls into that bracket is taxed at the higher rate. Another myth is that tax brackets are set in stone and never change. Wrong again. The brackets are adjusted annually for inflation, so they can shift from year to year.
Myth vs. Reality
Here’s a quick breakdown of some common myths and the reality behind them:
- Myth: Moving into a higher tax bracket means you’ll take home less money.
- Reality: Only the portion of your income that falls into the higher bracket is taxed at that rate. The rest stays the same.
- Myth: Tax brackets never change.
- Reality: The brackets are adjusted annually for inflation, so they can shift from year to year.
See? Not all the rumors you hear are true. It’s important to know the facts so you can make informed decisions.
Strategies to Optimize Your Tax Bracket
Now that you understand how tax brackets work, let’s talk about how you can optimize them to your advantage. There are several strategies you can use to lower your taxable income and stay in a lower bracket—or at least avoid jumping into a higher one.
Contribution to Retirement Accounts
One of the best ways to lower your taxable income is by contributing to retirement accounts like a 401(k) or IRA. These contributions are often tax-deductible, which means they reduce your taxable income. For example, if you earn $50,000 and contribute $5,000 to your 401(k), your taxable income drops to $45,000. That could be enough to keep you in a lower tax bracket.
Tax Credits and Deductions
Another strategy is to take advantage of tax credits and deductions. Things like the child tax credit, mortgage interest deduction, and student loan interest deduction can all lower your taxable income. It’s like getting a discount on your taxes. Who doesn’t love a good deal?
How Tax Brackets Impact Investments
Tax brackets don’t just affect your paycheck—they also play a role in your investments. Depending on your bracket, the taxes you pay on investment income like dividends and capital gains can vary. This is where things can get a bit tricky, but don’t worry—we’ve got you covered.
Capital Gains Tax Rates
Capital gains are taxed differently depending on your tax bracket. If you’re in a lower bracket, you might pay 0% on long-term capital gains. But if you’re in a higher bracket, that rate can jump to 15% or even 20%. So, it’s important to consider your bracket when making investment decisions.
Future Changes to Tax Brackets
Nothing in life is certain except death and taxes—and even taxes can change. The tax brackets we have today might not be the same tomorrow. With new legislation and inflation adjustments, the brackets are constantly evolving. So, it’s important to stay informed and plan accordingly.
What to Expect in the Coming Years
Experts predict that tax brackets will continue to adjust for inflation, but there’s always the possibility of new laws or policy changes. For example, proposals to increase the top tax rate or add new brackets are always on the table. Keeping an eye on these changes can help you stay ahead of the game.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Taxes
So, there you have it—a deep dive into the world of tax brackets. Understanding how they work and how they impact your finances is key to making smart financial decisions. Whether you’re trying to save money, optimize your investments, or just make sense of your paycheck, knowing your tax bracket is a must.
Now, here’s the call to action: take what you’ve learned and put it into practice. Talk to a tax professional, review your finances, and make a plan. And don’t forget to share this article with your friends and family. Knowledge is power, and when it comes to taxes, the more you know, the better off you’ll be.
Table of Contents
Article Recommendations