Unpacking The Avian Flu: What You Need To Know
Hey there, folks! Let me drop this on you right off the bat—avian flu is no joke. It’s a global health issue that has been making headlines for years, and it’s something everyone should be aware of. Whether you're a poultry farmer, a pet bird owner, or just someone who likes to stay informed, understanding avian flu is crucial. So, buckle up because we're diving deep into the world of avian flu and breaking it down for you in a way that’s both informative and easy to digest.
You might be wondering, "What exactly is avian flu?" Well, it’s essentially a type of influenza virus that primarily affects birds, but here’s the kicker—it can sometimes jump to humans. This crossover is what makes it so concerning, especially when you consider the potential for widespread outbreaks. Let’s not sugarcoat it; the stakes are high, and being informed is your best defense.
Now, before we dive into the nitty-gritty, let me assure you that this isn’t just another doom-and-gloom article. We’re going to break down the facts, bust some myths, and give you practical tips to protect yourself and your feathered friends. Ready? Let’s get started.
Read also:Emma Slater And Sasha Farber Tie The Knot A Love Story To Remember
Table of Contents
- What is Avian Flu?
- A Brief History of Avian Flu
- How Does Avian Flu Spread?
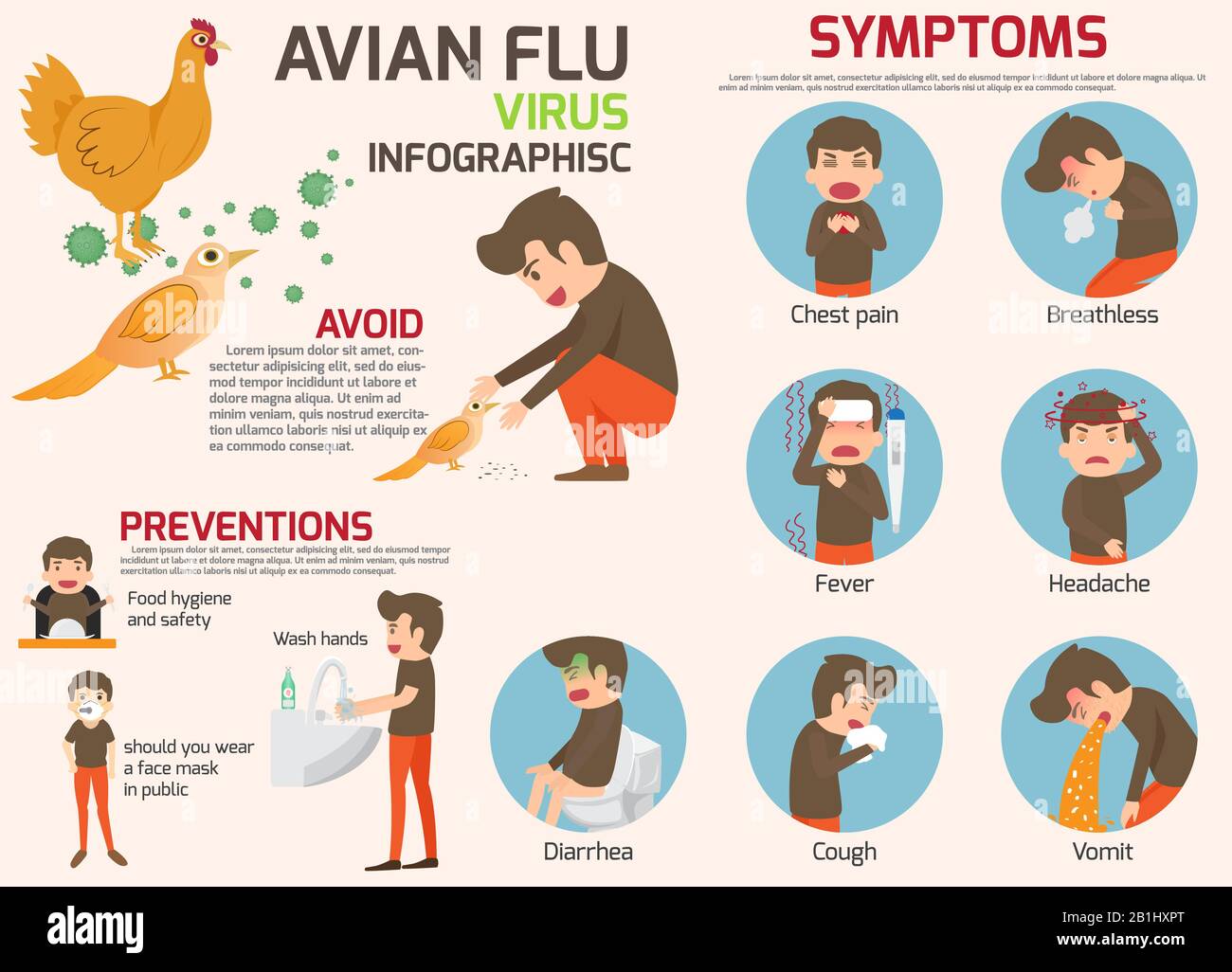
- Symptoms in Birds
- Human Infection: Fact vs. Fiction
- Prevention Tips for Farmers and Pet Owners
- The Global Impact of Avian Flu
- Vaccination Efforts: Are They Working?
- Debunking Common Myths About Avian Flu
- Looking Ahead: What’s Next for Avian Flu?
What is Avian Flu?
Alright, let’s start with the basics. Avian flu, also known as bird flu, is a highly contagious viral disease caused by influenza A viruses. These viruses are naturally found in wild aquatic birds, but they can also infect domestic poultry and other animals. The scientific term you’ll often hear is “H5N1,” which refers to one of the most common strains of avian flu. However, there are several other strains out there, each with its own level of severity.
Here’s the deal: avian flu isn’t just limited to birds. While it primarily affects our feathered friends, certain strains can cross over to humans, making it a public health concern. When this happens, it’s usually through direct contact with infected birds or contaminated surfaces. So, yeah, it’s not something to take lightly.
Why Should You Care?
Let me break it down for you. Avian flu isn’t just a problem for poultry farmers; it’s a global health issue. If left unchecked, it can lead to massive economic losses, food shortages, and even human fatalities. Plus, with the increasing interconnectedness of our world, an outbreak in one country can quickly spread to others. That’s why staying informed and taking preventive measures is so important.
A Brief History of Avian Flu
To truly understand the impact of avian flu, we need to look at its history. The first recorded outbreak of highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) was back in 1878 in Italy. Since then, there have been numerous outbreaks around the world, each one teaching us valuable lessons about how the virus behaves and spreads.
Fast forward to the late 1990s, when the H5N1 strain made headlines after causing widespread outbreaks in Asia. This strain was particularly concerning because it showed the ability to infect humans, leading to several fatalities. Since then, global health organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) have been working tirelessly to monitor and control the spread of avian flu.
Key Milestones
- 1997: First human cases of H5N1 reported in Hong Kong.
- 2003-2004: Large-scale outbreaks in Asia, leading to millions of poultry deaths.
- 2014-2015: Outbreaks in North America, affecting millions of commercial poultry.
- 2021-2022: Recent outbreaks in Europe and North America, highlighting the ongoing threat.
How Does Avian Flu Spread?
Now, let’s talk about how avian flu spreads. It’s not rocket science, but it’s definitely something you should know. The virus is primarily transmitted through direct contact with infected birds or their bodily fluids, such as saliva, nasal secretions, and feces. Contaminated surfaces, water sources, and even airborne particles can also play a role in spreading the virus.
Read also:Jennifer Aniston And Justin Therouxs Dog Custody Battle Who Gets The Pups
Here’s a fun fact (or not-so-fun, depending on how you look at it): migratory birds are often blamed for spreading avian flu across continents. While they may carry the virus, it’s usually human activities—like transporting infected birds or improperly disposing of carcasses—that amplify the problem. So, yeah, it’s a complex issue with multiple factors at play.
Common Transmission Routes
- Direct contact with infected birds.
- Indirect contact through contaminated surfaces or equipment.
- Airborne transmission in enclosed spaces.
- Waterborne transmission in shared water sources.
Symptoms in Birds
When it comes to avian flu, recognizing the symptoms in birds is crucial. Early detection can help prevent the spread of the virus and minimize losses. So, what should you look out for? Here are some common signs:
- Sudden death without any apparent cause.
- Decreased appetite and energy levels.
- Swelling of the head, neck, and eyes.
- Diarrhea and respiratory issues.
- Drop in egg production or laying abnormal eggs.
It’s worth noting that not all strains of avian flu are equally deadly. Some may cause mild symptoms, while others can wipe out entire flocks in a matter of days. That’s why vigilance is key, especially for those working closely with birds.
Human Infection: Fact vs. Fiction
Okay, let’s address the elephant in the room: can humans really get avian flu? The short answer is yes, but it’s rare. Most human cases have been linked to direct contact with infected birds or contaminated environments. That being said, the risk of person-to-person transmission is extremely low, so you don’t need to panic.
Now, let’s talk about the symptoms. If a human does contract avian flu, they may experience flu-like symptoms such as fever, cough, sore throat, and muscle aches. In severe cases, it can lead to pneumonia and respiratory failure. However, it’s important to remember that these symptoms are similar to other respiratory infections, so proper testing is essential for diagnosis.
How to Protect Yourself
- Avoid close contact with live or dead birds, especially in areas where outbreaks have been reported.
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water after handling birds or poultry products.
- Cook poultry and eggs thoroughly to kill any potential viruses.
- Seek medical attention if you develop flu-like symptoms after exposure to birds.
Prevention Tips for Farmers and Pet Owners
For those working with birds, prevention is key. Whether you’re a commercial farmer or a backyard chicken enthusiast, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk of avian flu. Here are a few tips:
- Implement strict biosecurity measures, such as limiting access to your property and disinfecting equipment regularly.
- Monitor your birds closely for any signs of illness and report suspicious cases to authorities immediately.
- Provide clean water and feed, avoiding contamination from wild birds or other animals.
- Consider vaccinating your flock if it’s available and recommended in your area.
Remember, prevention isn’t just about protecting your birds; it’s about safeguarding your livelihood and the community at large. Taking proactive steps can make a huge difference in controlling the spread of avian flu.
The Global Impact of Avian Flu
When you zoom out and look at the bigger picture, the impact of avian flu is staggering. Economically, it has caused billions of dollars in losses for the poultry industry. Socially, it has raised concerns about food security and public health. And environmentally, it has highlighted the need for better wildlife management practices.
But here’s the thing: we’re not powerless against this threat. Thanks to advances in science and technology, we’re better equipped than ever to monitor, control, and mitigate the spread of avian flu. From rapid diagnostic tests to global surveillance networks, we have the tools to stay ahead of the curve.
Global Efforts
- Collaboration between governments, NGOs, and international organizations to share data and resources.
- Investment in research and development of vaccines and antiviral drugs.
- Public awareness campaigns to educate people about prevention and control measures.
Vaccination Efforts: Are They Working?
Vaccination is often touted as a key strategy in combating avian flu, but how effective is it really? The truth is, it depends on the strain and the specific circumstances. Some vaccines have shown promising results in reducing the severity of outbreaks, but they’re not a silver bullet.
One of the challenges with avian flu vaccines is that the virus can mutate rapidly, making it difficult to keep up. This is why ongoing research and surveillance are so important. Scientists are constantly working to develop new and improved vaccines that can better protect both birds and humans.
Debunking Common Myths About Avian Flu
Let’s clear up some misconceptions about avian flu because, let’s face it, the internet can be a breeding ground for misinformation. Here are a few myths you might have heard:
- Myth: Eating cooked chicken can give you avian flu. Fact: Cooking poultry to the proper temperature kills the virus, making it safe to eat.
- Myth: Avian flu is easily transmissible between humans. Fact: Person-to-person transmission is extremely rare and typically requires prolonged close contact.
- Myth: Vaccines for avian flu are 100% effective. Fact: While vaccines can reduce the severity of outbreaks, they’re not foolproof due to the virus’s ability to mutate.
Looking Ahead: What’s Next for Avian Flu?
As we look to the future, it’s clear that avian flu will remain a challenge for years to come. However, with continued research, collaboration, and vigilance, we can minimize its impact. Advances in technology, such as gene editing and artificial intelligence, hold promise for developing more effective vaccines and diagnostic tools.
But here’s the bottom line: it’s up to all of us to do our part. Whether you’re a farmer, a scientist, or just an ordinary citizen, staying informed and taking preventive measures can make a big difference. Together, we can protect our birds, our health, and our planet.
Kesimpulan
To sum it all up, avian flu is a complex and ever-evolving threat that requires our attention and action. By understanding how it spreads, recognizing the symptoms, and implementing preventive measures, we can reduce its impact on both animals and humans. Remember, knowledge is power, and staying informed is your best defense.
Article Recommendations