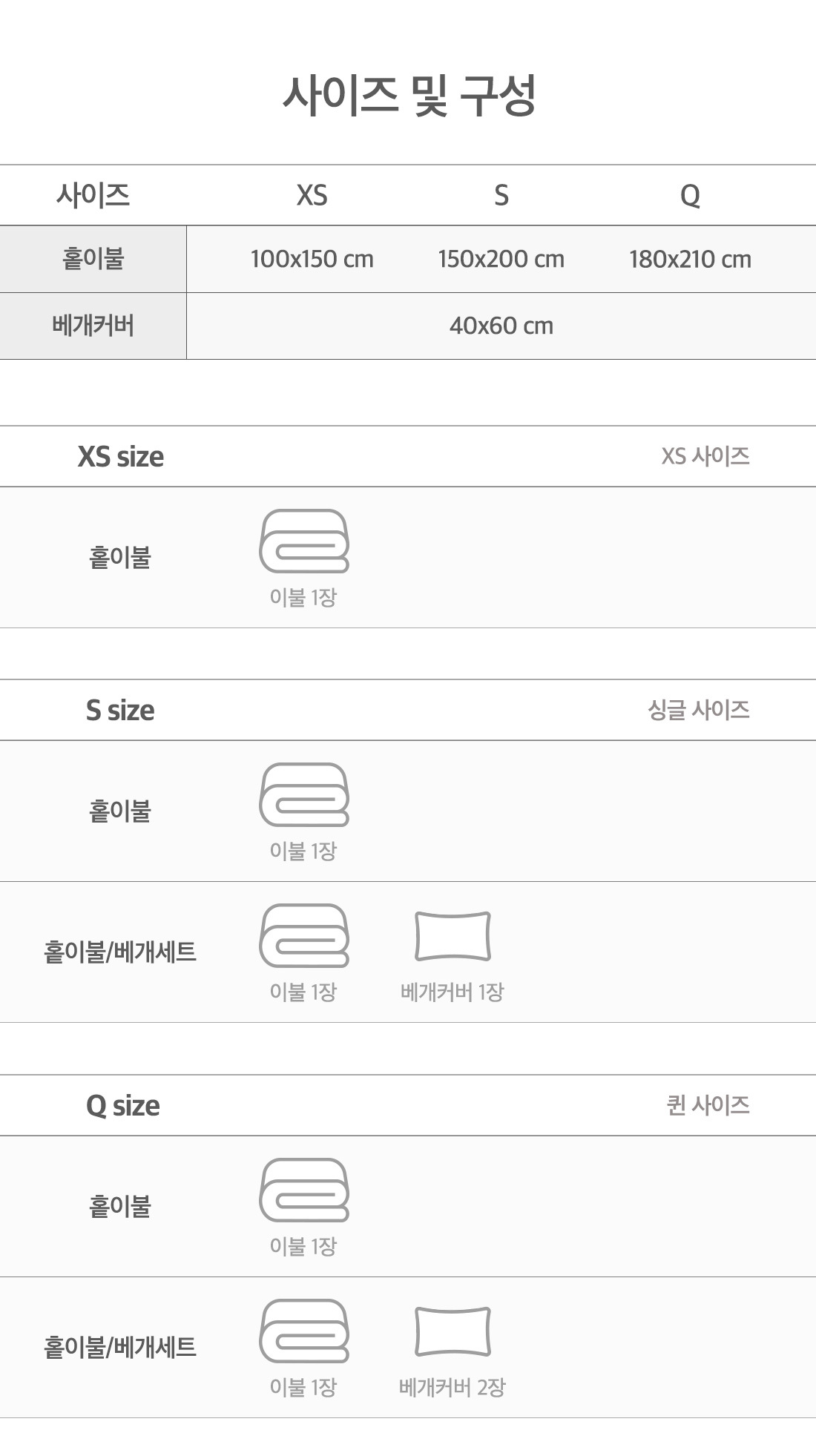
What Is Ice? Exploring The Frozen Wonder Around Us
Ice, the magical solid form of water, has been a part of our lives for centuries. From the frosty peaks of mountains to the cubes in your favorite drink, ice plays a crucial role in our daily existence. But have you ever stopped to think about what exactly ice is and how it forms? Let's dive into this fascinating topic and uncover the secrets behind this frozen marvel. Prepare yourself for a journey into the world of ice, where science meets wonder.
Ice is more than just a frozen cube in your glass. It's a fundamental element that shapes our planet's climate and ecosystems. Understanding ice goes beyond simple curiosity—it's essential for comprehending global weather patterns and environmental changes. So, whether you're a science enthusiast or just someone who loves a cold drink, there's something here for everyone.
As we explore the wonders of ice, we'll uncover its properties, formation, and the impact it has on our world. This isn't just about frozen water; it's about the science, history, and significance of a substance that affects every corner of the globe. So, let's get started and uncover the secrets behind this incredible natural phenomenon.
Read also:Prince Harry And Meghan Markles Pda Royal Drama Unfolds
The Science Behind Ice Formation
When it comes to ice, the science is as cool as the subject itself. Water molecules, which normally dance around freely in liquid form, slow down as temperatures drop. Once the temperature reaches 0 degrees Celsius (32 degrees Fahrenheit), these molecules lock into a hexagonal lattice structure, forming solid ice. This transformation isn't just a physical change; it's a chemical marvel that has fascinated scientists for generations.
How Temperature Affects Ice Formation
Temperature plays a critical role in the creation of ice. In fact, the freezing point of water can vary slightly depending on impurities and pressure. For instance, saltwater freezes at a lower temperature than freshwater, which is why ocean ice behaves differently from freshwater ice. These variations make ice formation a complex and intriguing process.
- Water freezes at 0°C under standard conditions.
- Impurities like salt can lower the freezing point.
- Pressure can also influence how water transforms into ice.
What Makes Ice Unique?
Ice isn't just frozen water; it's a substance with unique properties that set it apart from other solids. For starters, ice floats on water because it's less dense in its solid form. This characteristic is vital for life on Earth, as it allows aquatic creatures to survive in frozen lakes and rivers. Additionally, ice has the ability to reflect sunlight, which plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth's climate.
The Density Mystery
One of the most fascinating aspects of ice is its lower density compared to liquid water. This phenomenon occurs because of the open hexagonal structure that water molecules form when they freeze. As a result, ice expands and becomes buoyant, floating on the surface of water. This property is crucial for maintaining ecosystems in cold climates.
Ice in Nature: A Global Perspective
In the natural world, ice takes on many forms. From massive glaciers in Antarctica to delicate frost patterns on windows, ice shapes our planet in countless ways. These frozen wonders not only provide breathtaking scenery but also serve as vital indicators of climate change. By studying ice in nature, scientists can better understand the health of our planet and predict future environmental trends.
Glaciers: The Giants of Ice
Glaciers are enormous rivers of ice that flow slowly across landscapes. They are formed when snow accumulates over time, compressing into dense ice. These massive structures can be found in polar regions and high-altitude areas around the world. Glaciers play a crucial role in regulating global water supplies and are highly sensitive to changes in temperature.
Read also:Michael Caine Turns 85 A Legendary Life In Movies Family And Kindness
- Glaciers cover about 10% of the Earth's land surface.
- They store approximately 70% of the world's fresh water.
- Glacial melting contributes significantly to rising sea levels.
Ice in Daily Life
Beyond its natural occurrences, ice is a staple in our daily lives. From keeping drinks cold to preserving food, ice serves practical purposes in households worldwide. Additionally, ice has cultural significance in various traditions and celebrations, such as ice sculpting and ice skating. Its versatility makes it an indispensable part of modern living.
Ice in Culinary Arts
In the culinary world, ice is more than just a cooling agent. Chefs use ice to enhance the presentation and taste of dishes. Techniques like flash freezing and ice sculpting have become popular in fine dining, showcasing the creative potential of this humble substance. Whether it's crafting intricate ice sculptures or chilling a refreshing cocktail, ice continues to inspire chefs and bartenders alike.
Ice and Climate Change
Ice is at the forefront of discussions about climate change. As global temperatures rise, ice sheets and glaciers are melting at unprecedented rates. This melting not only affects sea levels but also disrupts ecosystems and weather patterns worldwide. Understanding the relationship between ice and climate change is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate its impact.
The Melting Point
The Arctic and Antarctic regions are experiencing rapid ice loss, with some areas losing ice at a rate of several meters per year. This melting contributes to rising sea levels, which threaten coastal communities and habitats. Additionally, the loss of reflective ice surfaces reduces the Earth's ability to reflect sunlight, exacerbating global warming.
Historical Significance of Ice
Throughout history, ice has played a vital role in human civilization. From ancient ice harvesting techniques to the development of modern refrigeration, ice has been a key player in preserving food and extending shelf life. Its importance in trade and commerce cannot be overstated, as it allowed for the transportation of perishable goods across long distances.
Ice in Ancient Times
In ancient civilizations, ice was harvested from mountains and stored in ice houses to preserve food during warmer months. This practice was common in regions with cold winters and hot summers, such as China and Persia. The use of ice in preservation revolutionized food storage and distribution, laying the groundwork for modern refrigeration technologies.
Ice Sports and Recreation
Ice isn't just a scientific marvel; it's also a playground for sports and recreation. Activities like ice skating, hockey, and curling bring people together in pursuit of fun and competition. These sports rely on the unique properties of ice to create fast-paced and exhilarating experiences. Beyond organized sports, ice also provides a canvas for artistic expression through ice sculpting and ice climbing.
The Thrill of Ice Sports
Ice sports offer a unique blend of skill, speed, and strategy. Whether you're gliding across a rink in figure skates or battling for control of a puck in hockey, ice sports provide a rush of adrenaline and a sense of camaraderie. These activities not only promote physical fitness but also foster teamwork and discipline.
Ice in Popular Culture
Ice has captured the imagination of artists, writers, and filmmakers for generations. From classic tales of polar exploration to modern blockbusters featuring icy landscapes, ice continues to inspire creativity. Its portrayal in media often highlights themes of resilience, adventure, and the beauty of nature. Ice has become a symbol of purity and strength, resonating with audiences worldwide.
Ice in Movies and Literature
Films like "The Thing" and "Frozen" use ice as a backdrop for thrilling stories and breathtaking visuals. In literature, authors like Jack London and Jules Verne have woven ice into their narratives, creating vivid depictions of frozen worlds. These works not only entertain but also educate audiences about the wonders and challenges of life in icy environments.
Future of Ice: Challenges and Opportunities
As we look to the future, the fate of ice is closely tied to the health of our planet. Efforts to combat climate change and preserve ice formations are underway, but much work remains to be done. Innovations in technology and policy are essential for ensuring that future generations can experience the beauty and benefits of ice.
Innovative Solutions
Scientists and engineers are developing new methods to study and protect ice. Techniques such as satellite monitoring and drone technology allow researchers to gather data on ice conditions from remote locations. Additionally, initiatives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainable practices offer hope for slowing the loss of ice worldwide.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ice is much more than just frozen water. It's a vital component of our planet's ecosystems and a source of inspiration for science, culture, and recreation. By understanding the science behind ice and its role in shaping our world, we can appreciate its significance and work towards preserving it for future generations. So, the next time you enjoy a cold drink or marvel at a frozen landscape, take a moment to reflect on the wonders of ice.
Don't forget to share your thoughts in the comments below or explore other articles on our site. Together, let's continue to learn and grow in our appreciation of the natural world!
Table of Contents:
- The Science Behind Ice Formation
- How Temperature Affects Ice Formation
- What Makes Ice Unique?
- The Density Mystery
- Ice in Nature: A Global Perspective
- Glaciers: The Giants of Ice
- Ice in Daily Life
- Ice in Culinary Arts
- Ice and Climate Change
- The Melting Point
- Historical Significance of Ice
- Ice in Ancient Times
- Ice Sports and Recreation
- The Thrill of Ice Sports
- Ice in Popular Culture
- Ice in Movies and Literature
- Future of Ice: Challenges and Opportunities
- Innovative Solutions
Article Recommendations